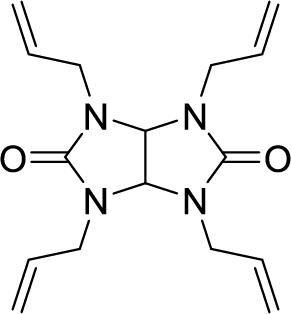
Low-dielectric Resin Cross-linker L-DAIC, DD-1
-
Can be used as an allyl cross-linker for polyphenylene ether resin and bismaleimide resin.
-
It can achieve lower Dk/Df than conventional cross-linking agents.
-
It is less volatile than conventional allyl cross-linking agents and can suppress composition changes and equipment contamination during curing.
-
-
-
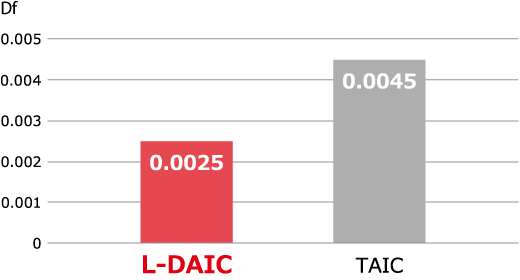
Dissipation Factor Comparison
Achieves lower dielectric loss tangent than conventional allyl crosslinkers
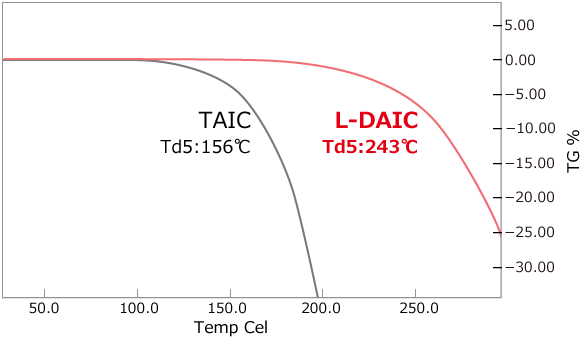
Volatility Comparison
Higher boiling point and lower volatility than conventional allyl cross-linkers
Application
-

Low Dielectric Laminated Materials
Low Dielectric Films
Low Dielectric Encapsulant -

Adhesives for electronic materials
Adhesive films
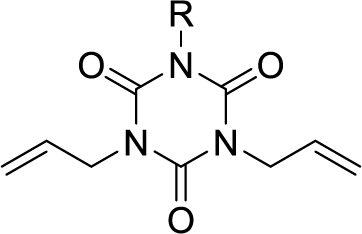
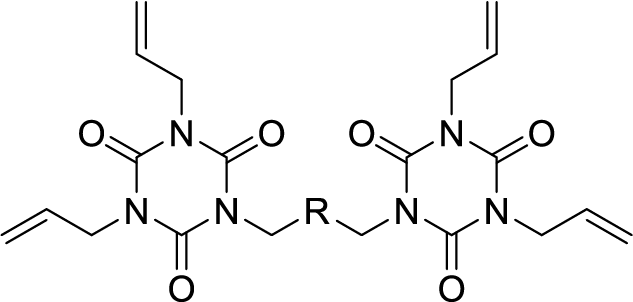
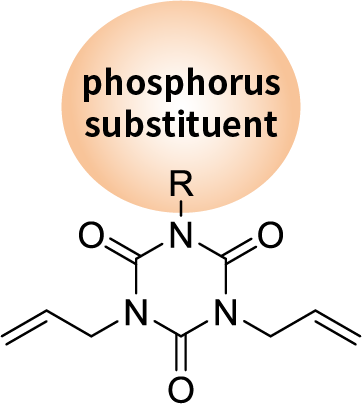
Low-dielectric, flame-retardant cross-linker P-DAIC (Under Development)
-
Can be used as an allyl cross-linker for polyphenylene ether resin and bismaleimide resin.
-
It can achieve lower Dk/Df than conventional cross-linking agents.
-
It is possible to achieve both flame retardancy andmechanical strength (adhesion), which have been issues in the past.
-
Application
-

Low Dielectric Laminated Materials
Low Dielectric Films
Low Dielectric Encapsulant -

Adhesives for electronic materials
Adhesive films
This product is on an exploratory basis and future supply is not guaranteed.
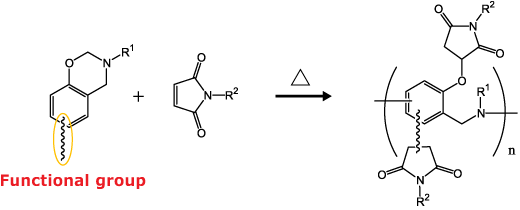
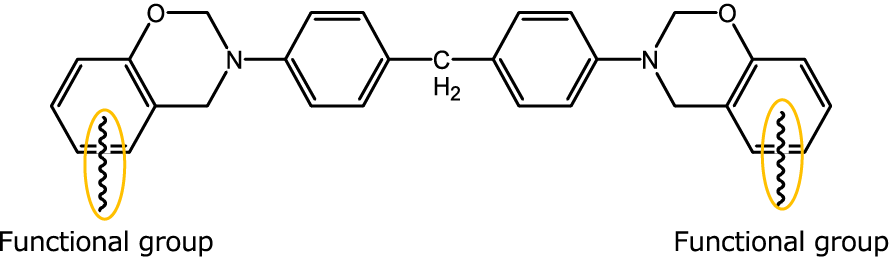
Low-dielectric Bismaleimide (BMI) Resin Cross-linker Benzoxazine ALP-d, P-d
-
Benzoxazine react with bismaleimide resin and is suitable as a cross-linking agent.
-
The dielectric loss tangent can be improved compared to conventional cross-linking agents.
-
It can improve curability and mechanical properties, which have been issues with bismaleimide resins.
-
-
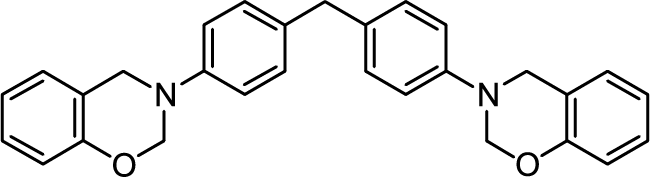
-
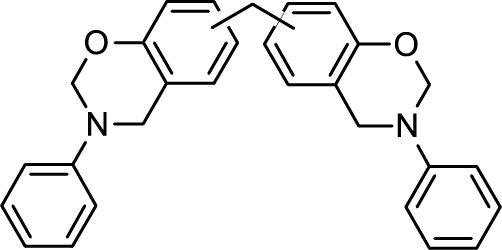
Benzoxazine/BMI cross-linking reaction
Phenolic hydroxyl groups generated by benzoxazine ring-opening react with BMI to form a cross-linked structure.